Risk oversight and the control system
Although it has a limited economic and financial risk profile because most of its operations are in regulated business segments, Snam adopts a structured and systemic approach to governing all risks that could affect value creation.
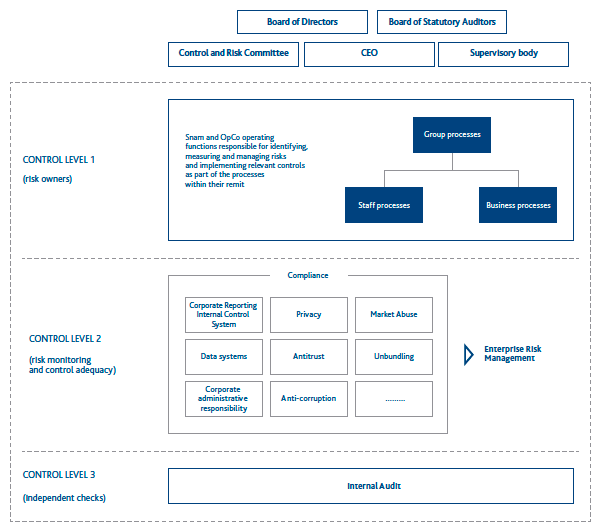
The system we use across the Group to identify, assess, manage and control risk has three levels, each with different objectives and associated responsibilities. The Board of Directors charges the CEO with giving structure to and maintaining the entire system.
More information on how we manage and mitigate the major risks we face can be found in section “Mitigation of environmental, health and safety impacts” of this Report.
We use an integrated, dynamic and group-wide method of assessing risk that evaluates the existing management systems in the individual corporate processes, starting with those relating to the prevention of fraud and corruption and health, safety, environment and quality.
These same controls form an integral part of the managerial processes. Management must therefore foster an environment that encourages controls, and must specifically manage “line controls”, consisting of all the control activities that individual operating units or companies perform over their own processes. Independent controls are performed by the Internal Audit department, which is responsible for checking that the system is functioning and adequate.
Type of capital |
Description and specific reference to the Snam model |
Reference in the Directors’ Report |
Financial |
The fundamental input for making investments in gas system infrastructure. We fund these investments using our own resources and debt capital obtained either on the financial markets or through our own operating income |
|
Manufactured |
The network of infrastructure for transporting, storing and distributing natural gas and regasifying LNG, required to perform services for operators and users |
|
Intellectual |
Unique to Snam, this consists mainly of the IT systems, procedures and good operating practices developed over time by managing the business |
|
Human |
This includes the specific skills and experience acquired by our staff, primarily by way of internal development programmes (this is essentially a self-made capital), and the business culture with its distinctive values, above all a culture of safety |
|
Social and relationship |
This is the licence to operate that the stakeholders award to Snam, sustained by relations with these stakeholders at European and national levels, as well as by Snam’s presence in the areas that host its infrastructure |
|
Natural |
The land, air and biodiversity that Snam is committed to preserving through efficient and responsible environmental management, mitigating the environmental impacts and consequences generated predominantly during the construction of infrastructure |
|
|
|
|
Legend |
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
Value dynamics and timelines |
Value creation methods |
Main operating activities |
Reference in the Directors’ Report |
In the short term, value creation is tied to the ordinary performance of corporate activities in accordance with the methods prescribed by rules and procedures, particularly in relation to risk management the main point of reference is the annual budget. In the medium term, the ability to carry out investment programmes, thereby ensuring a flow of resources and that favourable economic conditions are maintained, is also important. The main point of reference is the Business Plan, which covers a period of four years. In the long term, it is vital that the investment decisions and strategic choices made have interpreted trends in the best way possible. The main point of reference is the infrastructure development plan submitted to the Authority, which covers a period of 10 years. |
Maintaining the efficiency and availability of the network |
Executing the scheduled works |
|
Maintenance |
|||
Controls and inspections |
|||
Service quality and continuity |
Compliance with the network codes |
|
|
Preventing and mitigating risks and detrimental outside forces |
Managing financial risks |
|
|
Managing operating risks |
|||
Managing partnership portfolios |
|||
Managing crises |
|||
Preventing accidents |
|||
Mitigating environmental impact |
|||
Consistent Investment flows |
Planning infrastructure development |
|
|
Obtaining financial resources on the market |
|||
Permissions |
|||
Maintaining and developing human and relationship capital |
Relationships with the authorities |
|
|
Managing the supply chain in relation to the development of construction sites |
|||
Developing roles and capabilities |
|||
Managing relations with local communities |
|||
Ensuring that strategic direction and development plans are consistent with the environment in the reference sector |
Planning infrastructure development |
|
|
External growth |
|||
|
|
|
|
Legend |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||