The global energy context: The global energy context: Snam's key role in decarbonisation

Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC):
average global temperatures to date of around 1°C compared with pre-industrial levels
The strong correlation between human activity and global warming is increasingly visible and tangible especially through the recent increase in temperature, extreme weather conditions and the weakening or destruction of entire ecosystems.
This connection was also confirmed by the latest report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which revealed an increase of average global temperatures to date of around 1°C compared with pre-industrial levels (projected to be +1.5°C between 2030 and 2052) and the data and estimates of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), from which it emerges that in 2018 global atmospheric concentrations of the major greenhouse gases reached record levels (407.8±0.1 parts per million of CO2, corresponding to a rise of 147% compared with pre-industrial levels).
In response to this situation, legislative arrangements were made during UN conference on climate change, known as COP25, which was held in Madrid from 2 to 15 December 2019, in order to achieve the three main climate targets defined during the climate conference in Paris (COP21): to reduce emissions by 45$ by 2030, to achieve climate neutrality by 2050 and to stabilise the increase in global warming to 1.5° C.
Later on, in the European Green Deal of December 2019, the European Commission defined a collection of measures aimed at achieving climate neutrality by 2050. Specifically, this communication require gas system infrastructures to: i) embrace renewable gases; ii) support, jointly with the electricity industry, the energy system (sector coupling); iii) support sustainable mobility services.
In this context, Snam has developed future energy scenarios in which it has outlined its business strategy in line with the European and national decarbonisation objectives and with an ever increasing commitment to energy transition.

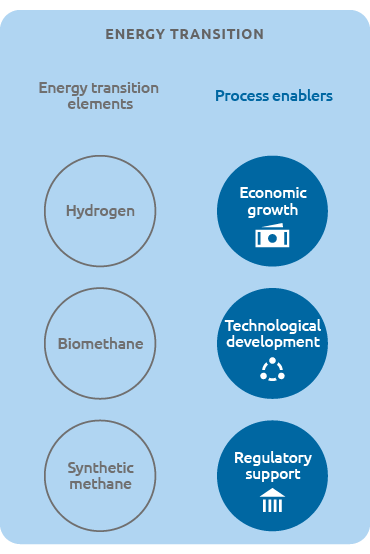
In conjunction with Terna, Snam has developed the “Document Describing the 2019 Scenarios”, a preliminary study for the preparation of transmission and transportation network development plans in the electricity and gas sectors nationally. This study develops joint Snam-Terna energy scenarios showing how technological development together with collaboration and synergies between the electricity and gas industries could be the key for reaching the emission reduction targets. The scenarios put forward, in a context of economic growth, highlight how the European decarbonisation objectives will lead to the increasing use of green gases, such as hydrogen, biomethane and synthetic methane, partly replacing natural gas, not only in thermoelectric power plants, but also in end uses: civil, industrial and transport.
Among the various energy sources of the future, Snam is looking at the new frontier of hydrogen developing, with the analytical support of a leading consultancy firm, the “Hydrogen potential” scenario that evaluates the potential of hydrogen as a vector for energy transition in Italy highlighting a key role for achieving the decarbonisation targets. The scenario estimates that by 2050 hydrogen could satisfy 23% of total energy demand in Italy. According to this study, hydrogen will be increasingly competitive in terms of costs compared with alternative energy sources, especially in sectors such as, for example, transport, heating and high-temperature industrial processes.
According to this study, hydrogen will be increasingly competitive in terms of costs compared with alternative energy sources, especially in sectors such as, for example, transport, heating and high-temperature industrial processes
In this historical period of change in global energy equilibrium, Snam recognises its leading role in achieving national and European undertakings and, in accordance with the targets set in its own Strategic Plan for the coming years, is supporting the country’s journey for mitigating the effects of climate change.