Biomethane
The development of the biomethane sector from agricultural production represents a strategic opportunity for Snam, allowing it to consolidate and strengthen its energy transition objectives, as well as have a positive impact on the entire agri-food sector, promoting a sustainable and circular economic model, and significantly reducing emissions in the agricultural and agri-livestock sector.
For the 2020-2024 Plan, biomethane investments amount to approximately Euro 220 million by 2024 and include the construction of infrastructure and plants with an installed capacity of 64 MW, 22 more than the previous Plan, as well as the development of a platform for growth in the circular economy and the industrialisation of agricultural production. In addition, part of the investments is allocated to the acquisition of companies active in the production of biomethane, to internalise expertise and seize additional growth opportunities. As also formalised in the ESG Scorecard, Snam plans to increase biomethane production to 141 million cubic metres by 2023. In 2020, the first steps were taken in this direction, and 0.44 million cubic metres were produced.
To achieve these objectives, since 2018, Snam has been using the technical expertise of its subsidiary IES Biogas, which builds, upgrades and maintains biomethane plants in the food, waste and agricultural sectors. During 2020, plants were designed and built to produce advanced biomethane from food industry waste and by-products and from waste, in particular from FORSU, the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste. Specifically, in addition to the conversion of existing plants to biomethane, four new plants have been built in Veneto, Lombardy and Sicily to produce biomethane as an alternative fuel for vehicles. Furthermore, IES Biogas has also been involved in the design and construction of various plants for the production of advanced biomethane from livestock waste, agro-industrial waste, agricultural by-products and second-harvest crops.
Biogas and biomethane
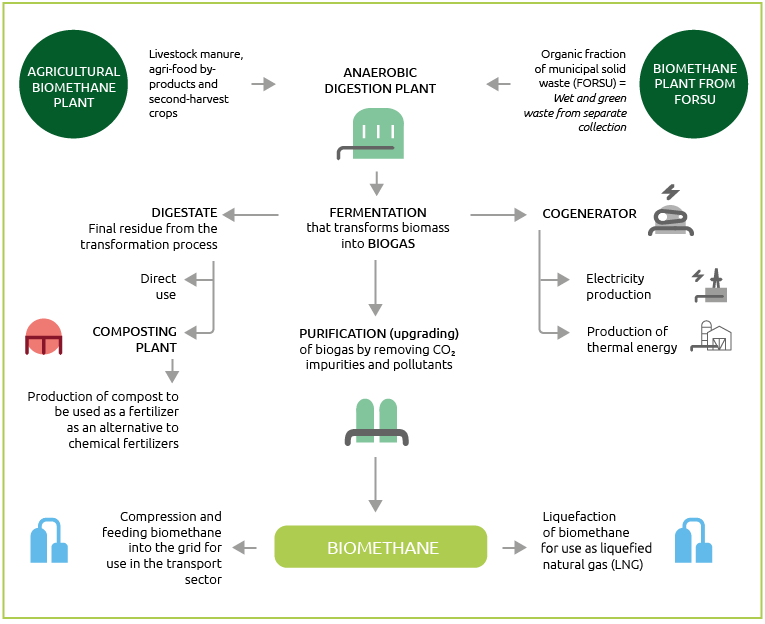
Biogas is one of the most widely used alternative sources of renewable energy. It is the result of the fermentation of organic substances (animal or vegetable) by numerous bacteria in the absence of oxygen and at a controlled temperature. This process of biomass degradation (from agricultural residues, livestock or sewage effluents, supplementary crops, organic fraction of separately collected municipal waste, etc.) is called anaerobic digestion.
Biomethane is a gas derived from biogas that has undergone a refining and purification process, known as upgrading, whose methane or CH4 concentration exceeds 98%. Biomethane is therefore renewable because it is produced from agricultural biomass, and sustainable because it is CO2 neutral.
With a view to growing by internalising the technical expertise of leading companies in the sector, in 2020, through its subsidiary Snam4Environment, Snam finalised the acquisition of Renerwaste S.r.l., a company active in biogas and biomethane infrastructure that operates through three plants located in the provinces of Lodi, Milan and Tortona. The Group also completed the acquisition of 50% of Iniziative Biometano, a company operating in Italy in the management of biogas and biomethane plants fuelled by biomasses of agricultural origin and owner of five biogas plants already in operation for which the conversion to biomethane is planned, thanks to IES Biogas, with a total potential production at full capacity of about 39 MW. The first of these, in Sicily, went into production in October. Snam also continued the project with Enersi Sicilia S.r.l., 100% acquired in 2018, which envisages the construction of a biomethane and compost production plant that will be used as natural fertiliser instead of chemical fertiliser. The facility, which will be completed in early 2021, will be able to recover 36,000 tonnes per year of FORSU, corresponding to approximately 3.2 million cubic metres of biomethane, equal to 30 GWh of energy produced per year, bringing numerous benefits to the area, including the creation of new jobs, skills, economic return for local businesses involved in the construction, support and supply of the new plant, as well as advantages for citizens in terms of reduced emissions and waste transport costs.
Agricultural biomethane and biomethane from FORSU plant